Occupations-Hackerrank
Pivot the Occupation column in OCCUPATIONS so that each Name is sorted alphabetically and displayed underneath its corresponding Occupation. The output column headers should be Doctor, Professor, Singer, and Actor, respectively.
Note: Print NULL when there are no more names corresponding to an occupation.
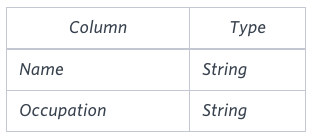
Input Format
The OCCUPATIONS table is described as follows:
Occupation will only contain one of the following values: Doctor, Professor, Singer or Actor.
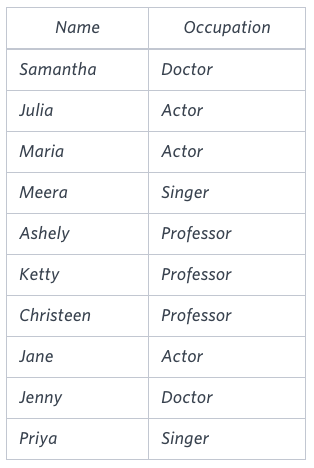
Sample Input
Sample Output
Jenny Ashley Meera Jane Samantha Christeen Priya Julia NULL Ketty NULL Maria
Explanation
The first column is an alphabetically ordered list of Doctor names.
The second column is an alphabetically ordered list of Professor names.
The third column is an alphabetically ordered list of Singer names.
The fourth column is an alphabetically ordered list of Actor names.
The empty cell data for columns with less than the maximum number of names per occupation (in this case, the Professor and Actor columns) are filled with NULL values.
Solution
To achieve the desired output, you can use a pivot query in SQL. Since SQL doesn't have an explicit PIVOT function in some databases (like MySQL), you can use a combination of CASE statements and ordering.
SELECT
MAX(CASE WHEN OCCUPATION = 'Doctor' THEN NAME END) AS Doctor,
MAX(CASE WHEN OCCUPATION = 'Professor' THEN NAME END) AS Professor,
MAX(CASE WHEN OCCUPATION = 'Singer' THEN NAME END) AS Singer,
MAX(CASE WHEN OCCUPATION = 'Actor' THEN NAME END) AS Actor
FROM (
SELECT NAME, OCCUPATION,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY OCCUPATION ORDER BY NAME) AS RowNum
FROM OCCUPATIONS
) AS Pivoted
GROUP BY RowNum
ORDER BY RowNum;
Explanation
ROW_NUMBER()Function:- Assigns a unique row number for each name within each
OCCUPATIONgroup. - The names are sorted alphabetically within each occupation using
ORDER BY NAME.
- Assigns a unique row number for each name within each
CASEwithMAX:- The
CASEstatements are used to pivot the rows into columns for each occupation (e.g.,Doctor,Professor, etc.). - The
MAXfunction ensures that only one name per row is selected for each occupation.
- The
Grouping by
RowNum:- Ensures that names with the same row number across different occupations appear on the same row in the output.
Handling NULL Values:
- If there are no names for an occupation at a specific row number,
NULLis returned automatically.
- If there are no names for an occupation at a specific row number,
Comments
Post a Comment